Independent Publishing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Self-publishing is the publication of media by its author at their own cost, without the involvement of a publisher. The term usually refers to written media, such as books and magazines, either as an
The Kindle Effect
Retrieved 9 November 2017, "...has become a $1 billion industry..." However, with the increased ease of publishing and the range of services available, confusion has arisen as to what constitutes self-publishing. In 2022, the Society of Authors and the Writers Guild of Great Britain produced a free downloadable guide to the various distinct types of publishing currently available.
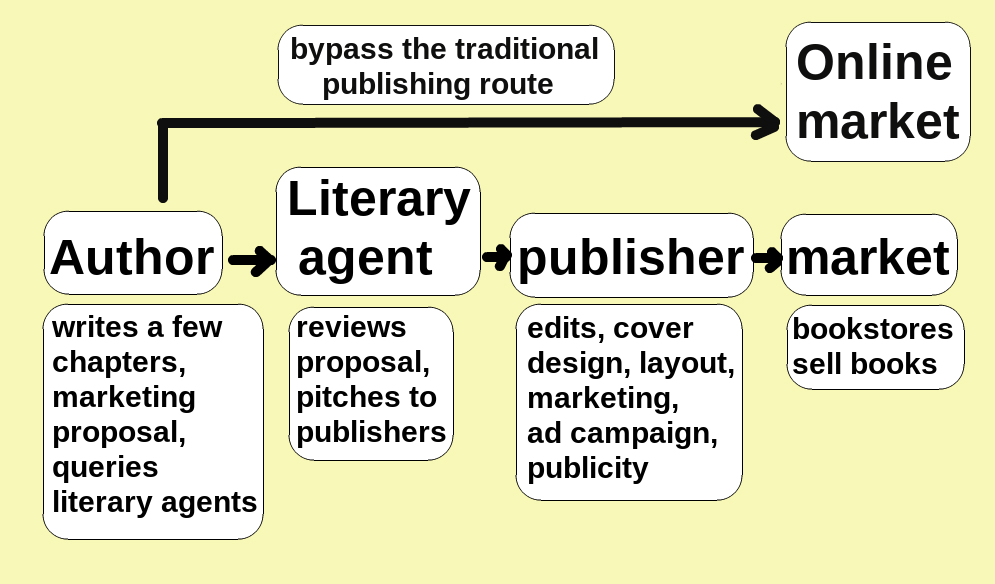 A huge impetus to self-publishing has been rapid advances in technology. Print-On-Demand (or POD) technology, which became available in the mid-1990s,Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America
A huge impetus to self-publishing has been rapid advances in technology. Print-On-Demand (or POD) technology, which became available in the mid-1990s,Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America
Self publishing
Retrieved 5 November 2017 makes it possible for a book to be printed after an order has been placed, so there are no costs for storing inventory. Further, the Internet provides access to global distribution channels via online retailers, so a self-published book can be instantly available to book buyers worldwide. Advances in e-book readers and tablet computers have improved readability, making ebooks more popular. Amazon's introduction of the ''Kindle'' and its self-publishing platform, '' Kindle Direct Publishing'' or KDP, in 2007 has been described as a tipping point in self-publishing, which "opened the floodgates" for self-publishing authors. The Espresso Book Machine (a POD device) was first demonstrated at the
The Espresso Book Machine (a POD device) was first demonstrated at the
Stealing Books in the Age of Self-Publishing: Many authors who sell their work directly on platforms like Amazon are having their stories plagiarized, which can take an emotional and financial toll.
Retrieved 31 October 2017, "...Rachel Ann Nunes ... First published in 1998, A Bid for Love did well enough to spawn two sequels ... Mullens' book, titled The Auction Deal, looked like the same story with much of the same language..."
 Kindle Direct Publishing or KDP is Amazon's e-book publishing unit ( see main article)
Kindle Direct Publishing or KDP is Amazon's e-book publishing unit ( see main article)
 While most self-published books do not make much money, there are self-published authors who have achieved sucess, particularly in the early years of online self-publishing. The number of authors who had sold more than one million e-books on Amazon from 2011 to 2016 was 40, according to one estimate.
* '' Fifty Shades of Grey'' by
While most self-published books do not make much money, there are self-published authors who have achieved sucess, particularly in the early years of online self-publishing. The number of authors who had sold more than one million e-books on Amazon from 2011 to 2016 was 40, according to one estimate.
* '' Fifty Shades of Grey'' by  * The breakout hit '' Wool'' by Hugh Howey was self-published originally and garnered more than a million dollars in royalty monies, and has generated over 5000 Amazon reviews.
* James Altucher's ''Choose Yourself'' (2013) sold 44,294 copies in its first month, debuted at No. 1 on Amazon's top non-fiction list, and was a ''Wall Street Journal'' bestseller.
*
* The breakout hit '' Wool'' by Hugh Howey was self-published originally and garnered more than a million dollars in royalty monies, and has generated over 5000 Amazon reviews.
* James Altucher's ''Choose Yourself'' (2013) sold 44,294 copies in its first month, debuted at No. 1 on Amazon's top non-fiction list, and was a ''Wall Street Journal'' bestseller.
*
ebook
An ebook (short for electronic book), also known as an e-book or eBook, is a book publication made available in digital form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Alt ...
or as a physical copy using POD (print on demand) technology. It may also apply to albums, pamphlets, brochures, games, video content, artwork, and zines. Web fiction is also a major medium for self-publishing.
Definitions
Although self-publishing is not a new phenomenon, dating back to the 18th century, it has transformed during the internet age with new technologies and services providing increasing alternatives to traditional publishing, becoming a $1 billion market.Jennifer Alsever, Fortune magazine, 30 December 2016The Kindle Effect
Retrieved 9 November 2017, "...has become a $1 billion industry..." However, with the increased ease of publishing and the range of services available, confusion has arisen as to what constitutes self-publishing. In 2022, the Society of Authors and the Writers Guild of Great Britain produced a free downloadable guide to the various distinct types of publishing currently available.
Self publishing vs. Hybrid Publishing and Vanity Publishing
In self publishing, authors publish their own book. It is possible for an author to single-handedly carry out the whole process. However increasingly, authors are recognizing that to compete effectively, they need to produce a high quality product, and they are engaging professionals for specific services as needed (such as editors or cover designers). A growing number of companies offer a one-stop shop where an author can source a whole range of services required to self-publish a book (sometimes called "Assisted Self-publishing Providers" or "Self-publishing Service Providers"). This should not be confused with * hybrid publishing, (where the publisher and author collaborate and ''share'' costs and risks. In return, the author may be required to surrender some control and/or rights in return for the publisher's financial and other contribution) OR *vanity publishing
A vanity press or vanity publisher, sometimes also subsidy publisher, is a publishing house where anyone can pay to have a book published.. The term "vanity press" is often used pejoratively, implying that an author who uses such a service is publ ...
, (where the author pays for the cost of all services, but also signs a restrictive contract which usually involves surrendering significant rights).
It has been suggested that the best test for whether a company offers "Assisted Self-publishing Services" or "Hybrid/vanity publishing" is to apply a variant of "Yog's Law", which states the following:
* Yog’s Law: Money flows ''toward'' the writer.
* Self-Publishing Corollary to Yog’s Law: While in the process of self-publishing, money and rights are ''controlled'' by the writer.
Therefore if a company offers services to the author without claiming any rights, and allows the author to control the entire process, they are assisting the author to self-publish. Whereas if the company takes some rights, and/or takes control of artistic decisions, they are a hybrid publisher or a vanity publisher, depending on the degree of involvement.
History
Early examples
Historically, some authors have chosen to self-publish. Successful examples areJohn Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
, Jane Austen
Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots of ...
, Emily Dickinson, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Martin Luther, Marcel Proust
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust (; ; 10 July 1871 – 18 November 1922) was a French novelist, critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel ''In Search of Lost Time'' (''À la recherche du temps perdu''; with the previous Eng ...
, Derek Walcott
Sir Derek Alton Walcott (23 January 1930 – 17 March 2017) was a Saint Lucian poet and playwright. He received the 1992 Nobel Prize in Literature. His works include the Homeric epic poem ''Omeros'' (1990), which many critics view "as Walcot ...
, and Walt Whitman. In 1759, British satirist Laurence Sterne's self-published the first two volumes of '' Tristram Shandy''. In 1908, Ezra Pound
Ezra Weston Loomis Pound (30 October 1885 – 1 November 1972) was an expatriate American poet and critic, a major figure in the early modernist poetry movement, and a Fascism, fascist collaborator in Italy during World War II. His works ...
sold ''A Lume Spento
''A Lume Spento'' (translated by the author as ''With Tapers Quenched'') is a 1908 poetry collection by Ezra Pound. Self-published in Venice, it was his first collection.
Background and writing
Ezra Pound (1885–1972) studied Romance languages ...
'' for six pence each. Franklin Hiram King's book ''Farmers of Forty Centuries'' was self-published in 1911, and was subsequently published commercially. In 1931, Irma S. Rombauer, the author of '' The Joy of Cooking'' paid a local printing company to print 3000 copies; the Bobbs-Merrill Company acquired the rights, and since then the book has sold over 18 million copies. In 1941, writer Virginia Woolf chose to self-publish her final novel '' Between the Acts'' on her Hogarth Press, in effect starting her own press.
Stigma
Traditional publishers are extremely selective in what they publish, and reject most of the manuscripts submitted to them. In spite of that rigorous selection, they then assign an editor to polish the work even further, a proof-reader to check for errors and a designer to produce the cover. With no support, a self-publishing author is very unlikely to produce a book to that professional standard, unless they are astonishingly talented. For that reason, self-published books have garnered a deserved reputation for being of lesser quality than mainstream books. Before the advent of the internet and POD (Print on Demand), most self-publishing authors had to resort to a vanity press, which was very costly and acted as a barrier to publication. Now, ebooks can be published at virtually no cost and the market has been flooded with poorly produced books. Some estimate that as much as 70% of published ebooks are so bad, they are unreadable. However, some self-published authors are now taking a professional approach, using services like critique groups, beta readerTechnological changes
 A huge impetus to self-publishing has been rapid advances in technology. Print-On-Demand (or POD) technology, which became available in the mid-1990s,Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America
A huge impetus to self-publishing has been rapid advances in technology. Print-On-Demand (or POD) technology, which became available in the mid-1990s,Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of AmericaSelf publishing
Retrieved 5 November 2017 makes it possible for a book to be printed after an order has been placed, so there are no costs for storing inventory. Further, the Internet provides access to global distribution channels via online retailers, so a self-published book can be instantly available to book buyers worldwide. Advances in e-book readers and tablet computers have improved readability, making ebooks more popular. Amazon's introduction of the ''Kindle'' and its self-publishing platform, '' Kindle Direct Publishing'' or KDP, in 2007 has been described as a tipping point in self-publishing, which "opened the floodgates" for self-publishing authors.
 The Espresso Book Machine (a POD device) was first demonstrated at the
The Espresso Book Machine (a POD device) was first demonstrated at the New York Public Library
The New York Public Library (NYPL) is a public library system in New York City. With nearly 53 million items and 92 locations, the New York Public Library is the second largest public library in the United States (behind the Library of Congress ...
in 2007. This machine prints, collates, covers, and binds a single book. It is in libraries and bookstores throughout the world, and it can make copies of out-of-print editions. Small bookstores sometimes use it to compete with large bookstore chains. It works by taking two pdf
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
files, one for the text and one for the cover, and then prints an entire paperback book in a matter of minutes, which then drops down a chute.
The ''Library Journal
''Library Journal'' is an American trade publication for librarians. It was founded in 1876 by Melvil Dewey. It reports news about the library world, emphasizing public libraries, and offers feature articles about aspects of professional prac ...
'' and Biblioboard worked together to create a self-publishing platform called Self-e in which authors submitted books online which were made available to readers. These books are reviewed by ''Library Journal'', and the best ones are published nationwide; authors do not make money this way but it serves as a marketing tool.
Advantages of self-publishing
# Speed. In traditional publishing, an author must first find an agent, then the agent must find a publisher, then it may take a year or more for the book to go through editing and be allocated a 'slot' in the publisher's calendar. With self-publishing, it is possible to release a book within a few weeks after it is finished. # No start-up costs. It costs nothing to upload a book to most publishing platforms, and print copies do not have to be paid for until a customer orders. # Artistic control. A traditional publisher may demand changes to meet market demands. # Control on pricing. The author decides the price and can change at any point of time. # A greater share of royalties. Self-published authors may earn four to five times more per unit than if an author works with a traditional publisher, sometimes 70 percent of the sale price. # Pitch books straight to the readers. There is no intermediary censoring what might be shown to the public. The route to readers is more direct.Disadvantages of self-publishing
#Stigma. Self-published books still have to combat prejudice due to the lack of gatekeepers to ensure quality. # No physical presence. Traditional publishers distribute their books to high street bookstores on a sale-or-return basis, which is unaffordable for a self-published author, and libraries routinely order from the publisher's catalogues. # No advance. Traditional publishers will usually pay an advance, so the author receives some payment for the book even if it is unsuccessful. # No free support. Traditional publishers pay all the costs associated with producing the book, and will provide an editor and cover designer at their expense. # Cost. The obvious corollary of the above is that the self-published author must pay all their own expenses. Though it is possible to publish a book free of charge, marketing and promotion are expensive. # Marketing and promotion are time-consuming and costly. Marketing is a task that many authors are not skilled at. UK author Rachel Abbott was working "14-hour days" promoting her book ''Only the Innocent''; while she eventually made it to the UK Kindle bestseller chart, she still had difficulty getting the publishing world to take her book seriously. Another writer, Ros Barber, thinks self-publishing is a "terrible idea for serious novelists" since the requirements of marketing and promoting a book will prevent one from writing, and he continues to recommend the traditional approach. #Plagiarism
Plagiarism is the fraudulent representation of another person's language, thoughts, ideas, or expressions as one's own original work.From the 1995 '' Random House Compact Unabridged Dictionary'': use or close imitation of the language and thought ...
. It is relatively easy to download the text of an ebook and republish it with minor changes under a different title.The Atlantic, Joy Lanzendorfer, 6 June 2016Stealing Books in the Age of Self-Publishing: Many authors who sell their work directly on platforms like Amazon are having their stories plagiarized, which can take an emotional and financial toll.
Retrieved 31 October 2017, "...Rachel Ann Nunes ... First published in 1998, A Bid for Love did well enough to spawn two sequels ... Mullens' book, titled The Auction Deal, looked like the same story with much of the same language..."
Publishing platforms
In order to be purchased by a customer, the completed book must be hosted on a publishing platform. Amazon's Kindle is the largest of these but there are others.Kindle Direct Publishing
 Kindle Direct Publishing or KDP is Amazon's e-book publishing unit ( see main article)
Kindle Direct Publishing or KDP is Amazon's e-book publishing unit ( see main article)
IngramSpark
IngramSpark lets authors publish digital, hardback and paperback editions of their books. It distributes books to most online bookstores. Bricks-and-mortar stores can also order books from IngramSpark at wholesale prices for sale in their own venues. It is run by Ingram Content Group.Apple
Apple sells books via its App Store which is a digital distribution platform for its mobile apps on its iOS operating system. Apps can be downloaded to its devices such as the iPhone, theiPod Touch
The iPod Touch (stylized as iPod touch) is a discontinued line of iOS-based mobile devices designed and marketed by Apple Inc. with a touchscreen-controlled user interface. As with other iPod models, the iPod Touch can be used as a music pl ...
handheld computer, and the iPad. Apple pays authors 70 percent of its proceeds at its Apple iBookstore where it sells iBooks.
Smashwords
Smashwords is a California-based company founded by Mark Coker which allows authors and independent publishers to upload their manuscripts electronically to the Smashwords service, which then converts them into multiple e-book formats which can be read on various devices.Barnes and Noble
Barnes & Noble
Barnes & Noble Booksellers is an American bookseller. It is a Fortune 1000 company and the bookseller with the largest number of retail outlets in the United States. As of July 7, 2020, the company operates 614 retail stores across all 50 U. ...
pays 65 percent of the list price of e-books purchased through its online store called Pubit.
Kobo
Kobo is a Canadian company which sells e-books, audiobooks, e-readers and tablet computers which originated as a cloud e-reading service.Scribd
Scribd is an open publishing platform which features a digital library, an e-book and audiobook subscription service.Lulu
Lulu is an online print-on-demand, self-publishing and distribution platform. GmbH BoD (2001), (since 1997 as ''Libri'' GmbH), is the "original" in self-publishing.Web fiction
A major development in this century has been the growth of web fiction. A common type is the web serial. Unlike most modern novels, web fiction novels are frequently published in parts over time. Web fiction is especially popular in China, with revenues topping US$2.5 billion, as well as in South Korea. Online literature in China plays a much more important role than in the United States and the rest of the world. Most books are available online, where the most popular novels find millions of readers. They cost an average of 2 CNY, or roughly a tenth of the average price of a printed book. Shanda Literature Ltd. is an online publishing company that claims to publish 8,000 Chinese literary works daily. Joara is S. Korea's largest web novel platform with 1.1 million members, 140,000 writers, an average of 2,400 serials per day and 420,000 works. Joara's users have almost the same gender ratio, and both fantasy and romance genres are popular.Self-published bestsellers
 While most self-published books do not make much money, there are self-published authors who have achieved sucess, particularly in the early years of online self-publishing. The number of authors who had sold more than one million e-books on Amazon from 2011 to 2016 was 40, according to one estimate.
* '' Fifty Shades of Grey'' by
While most self-published books do not make much money, there are self-published authors who have achieved sucess, particularly in the early years of online self-publishing. The number of authors who had sold more than one million e-books on Amazon from 2011 to 2016 was 40, according to one estimate.
* '' Fifty Shades of Grey'' by E.L. James
EL, El or el may refer to:
Religion
* El (deity), a Semitic word for "God"
People
* EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer
* El DeBarge, music artist
* El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ...
was originally published online as '' Twilight'' fan-fiction
Fan fiction or fanfiction (also abbreviated to fan fic, fanfic, fic or FF) is fictional writing written in an amateur capacity by fans, unauthorized by, but based on an existing work of fiction. The author uses copyrighted characters, setti ...
before the author decided to self-publish it as an e-book and print on demand.
* The science fiction novel '' The Martian'', by Andy Weir, was originally released as chapters on his personal blog, and then self-published as an eBook in 2011. The rights were purchased by Crown Publishing which re-released it in 2014; the novel went on to become a bestseller and then a major motion picture
Punchline is an American rock music, rock band from Belle Vernon, Pennsylvania, United States, that was formed in 1998. The band released its seventh full-length album, ''Thrilled (Punchline album), Thrilled'', on December 4, 2015, on InVogue R ...
starring Matt Damon.
* Blogger Alan Sepinwall's self-published book ''The Revolution Was Televised'' became an instant hit, winning a prominent review within two weeks of publication by critic Michiko Kakutani in '' The New York Times''. Sepinwall hired an editor and spent roughly $2,500 on services to get his book ready for publication.
* Minnesota social worker Amanda Hocking uploaded several books in 2010 and sold a few dozen copies. She published several more manuscripts and within a few months was making enough money to quit her daytime job. She later won a deal with Macmillan publishers, and went to being a millionaire in a year. She sold her series to St. Martin's Press in 2011 for two million dollars.
* Swedish author Carl-Johan Forssen Ehrlin wrote a book in 2010 which helped get children to go to sleep; his '' The Rabbit Who Wants to Fall Asleep'' title featured amateurish illustrations with "clunky prose" and a monotonous storyline, but parents bought it for the catchy subtitle of "A new way of getting children to sleep". He released it on CreateSpace and it became a bestseller.
* Erotic romance author Meredith Wild sold 1.4 million digital and print copies of her books, and founded her own publishing company called Waterhouse Press; she founded the firm in part because she felt that her novels were "not being taken seriously" as an indie author. An advantage of having her own imprint is that it is easier to get books into chainstores and big-box retailers.
 * The breakout hit '' Wool'' by Hugh Howey was self-published originally and garnered more than a million dollars in royalty monies, and has generated over 5000 Amazon reviews.
* James Altucher's ''Choose Yourself'' (2013) sold 44,294 copies in its first month, debuted at No. 1 on Amazon's top non-fiction list, and was a ''Wall Street Journal'' bestseller.
*
* The breakout hit '' Wool'' by Hugh Howey was self-published originally and garnered more than a million dollars in royalty monies, and has generated over 5000 Amazon reviews.
* James Altucher's ''Choose Yourself'' (2013) sold 44,294 copies in its first month, debuted at No. 1 on Amazon's top non-fiction list, and was a ''Wall Street Journal'' bestseller.
* Victoria Knowles
Victoria Knowles ( née Jenkins; born 16 April 1976) is an English author, actress, singer, producer and entrepreneur.
Career
''The PA'' and ''The PA's Story''
In June 2014, Knowles self-published an e-book titled ''The PA'', an autobiograp ...
achieved notoriety in July 2014 when her self-published book ''The PA'' reached the number one spot in the iTunes
iTunes () is a software program that acts as a media player, media library, mobile device management utility, and the client app for the iTunes Store. Developed by Apple Inc., it is used to purchase, play, download, and organize digital mul ...
chart for paid books.
* Matthew Reilly
Matthew John Reilly (born 2 July 1974) is an internationally bestselling Australian action thriller writer.
". Retrieved 10 ...
's self-published ''Contest'', the first of his action-thriller novels, in 1996.
". Retrieved 10 ...
See also
* Alternative media *Author mill An author mill is a publisher that relies on producing large numbers of small-run books by different authors, as opposed to a smaller number of works published in larger numbers. The term was coined by Victoria Strauss of Writer Beware, as a parall ...
* Dōjin
In Japan, is a group of people who share an interest, activity, or hobby. The word is sometimes translated into English as "clique", "fandom", "coterie", "society", or "circle" (as in "sewing circle"). Self-published creative works produced b ...
* Independent music
* List of self-publishing companies
* Samizdat
* Self Publish, Be Happy
* :Self-published books
* Small press
A small press is a publisher with annual sales below a certain level or below a certain number of titles published. The terms "indie publisher" and "independent press" and others are sometimes used interchangeably.
Independent press is general ...
* Predatory open access publishing
* Vanity publishing
A vanity press or vanity publisher, sometimes also subsidy publisher, is a publishing house where anyone can pay to have a book published.. The term "vanity press" is often used pejoratively, implying that an author who uses such a service is publ ...
* Web fiction
References
* {{Authority control Publishing